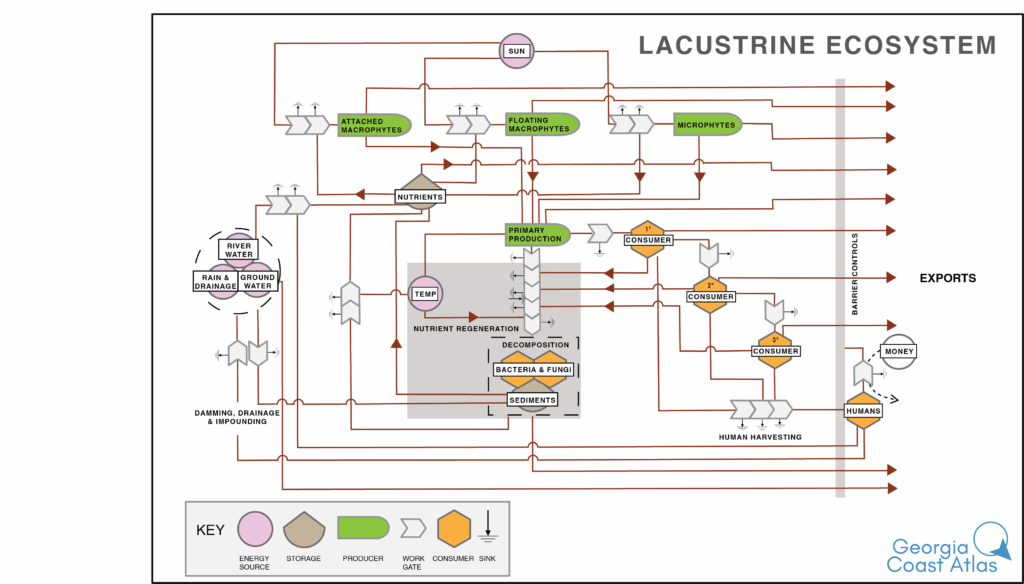
Diagram of energy flow and abiotic and biotic interactions in lacustrine ecosystems.
Lacustrine ecosystems are wetland and deepwater habitats that are in a topographic depression or a damned river channel. They often lack significant vegetation, and their water level is usually deeper than two meters. Subsystems include littoral and profundal zones. Littoral refers to shallow areas of bodies of water up to where sunlight can no longer penetrate the water to support plant life. Profundal zones refer to deeper water in lakes and reservoirs. The littoral zone supports rooted aquatic plants, algae, fish, and invertebrates, often with high productivity rates due to sunlight, sufficient nutrients, and oxygen. In the profundal zone, the water is colder with less oxygen and little to no plant life.