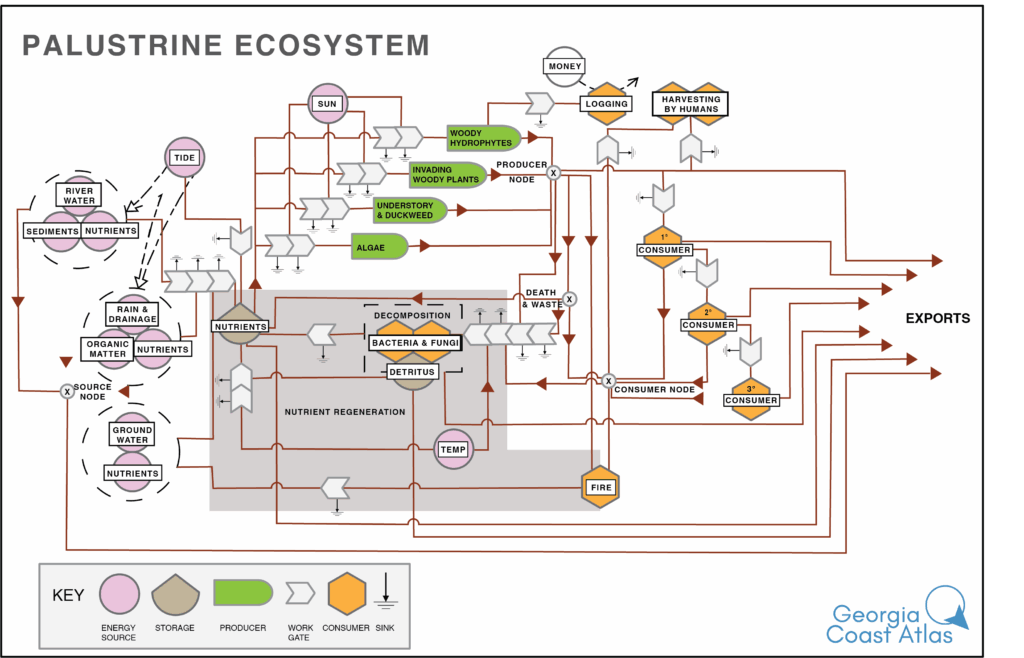
Palustrine ecosystems include all the non-tidal, primarily freshwater wetlands where, if present, water is shallow and does not typically flow as a stream. These swampy areas are often dominated by trees, shrubs, reeds, grasses, and other wetland plants. They are topographic regions characterized as depressions, floodplains, or areas along the edges of lakes and rivers. Palustrine ecosystems provide habitat for a wide range of wildlife, including amphibians, birds, and insects. Water levels may fluctuate seasonally depending on precipitation and groundwater levels. These wetlands play an essential role in water filtration and flood control, and catalyze biodiversity.
